SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor and Nagios XI are two SNMP monitoring suites, that offer a wide array of tools and features for making Network Monitoring & Management simple and efficient but there are other Nagios alternatives too.
This article will compare the two, and outline performance in key subject areas. The current version of SolarWinds at the time this article is written is 12.2.
The current version for Nagios is 5.4.11.
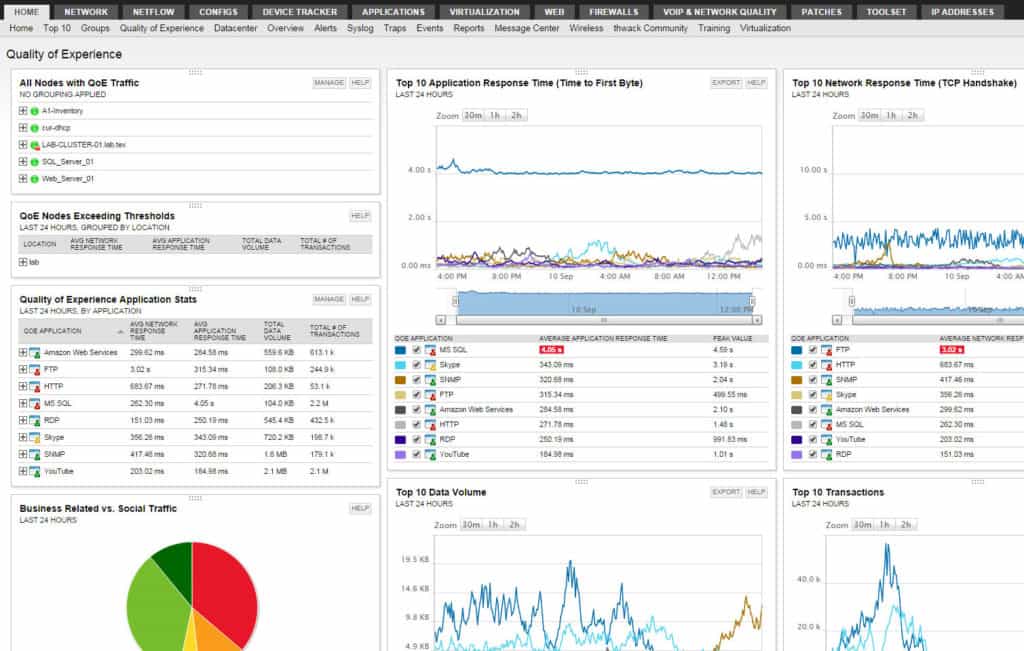
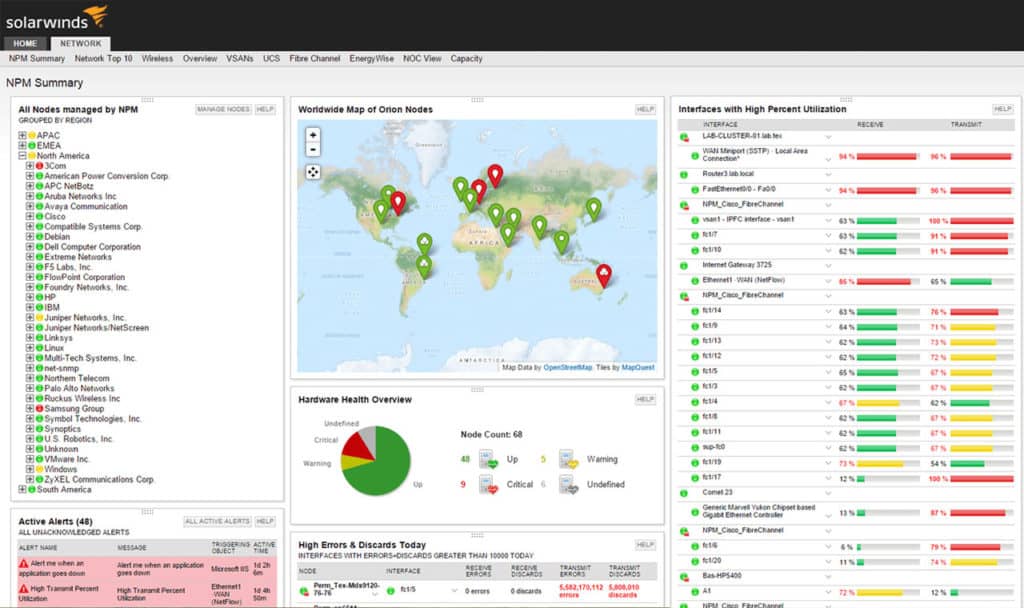
SolarWinds has a rather simple and straightforward install process.
That being said, there are a number of different base programs that SolarWinds offers which each have a separate focus and price.
For example, monitoring web servers with SolarWinds will require the Server and Application Monitor program, while mapping / topology requires the purchase and install of SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor program.
There are also a number of add-on modules for some of the base programs, that also come at a separate cost, like the Network Traffic Analyzer add-on for the Network Performance Monitor base program.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor for its comprehensive feature set that allows for quick detection and resolution of network issues. Its integration with NetPath and customizable intelligent alerts provide in-depth analysis and real-time responsiveness, making it a top-class monitoring tool.
Who is it recommended for?
SolarWinds NPM is best suited for IT professionals and network administrators who need exhaustive network monitoring capabilities. It’s particularly useful for large-scale enterprises with complex on-premises and cloud-based infrastructures, as well as for teams that rely on detailed reporting for network performance analysis.
Nagios is a little more complicated with regards to setup.
It can only run on CentOS or Red Hat Enterprise Linux, meaning that some basic CLI skills will be required.
To install, you will need to either download and install via command line, or download and mount a virtual hard drive in VMWare, VirtualBox, or Hyper-V.
If you mount a VHD, you will need to configure the network settings using the command line interface you are greeted with on first launch.
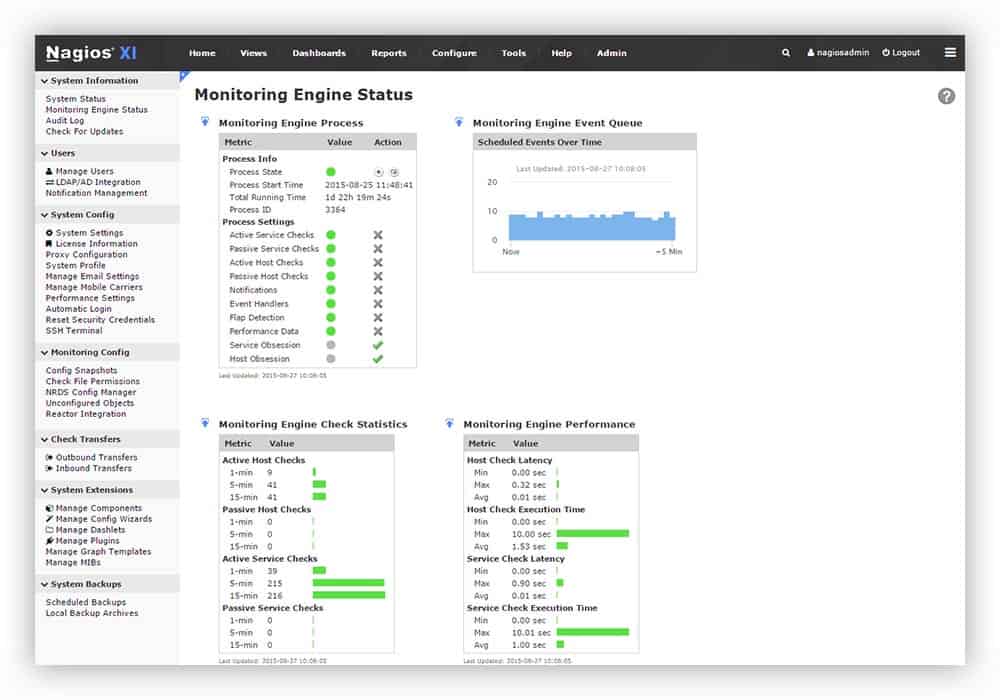
Nagios has a separate program called Nagios Network Analyzer, which is available for purchase separately from Nagios XI and provides further tools and features, but this article will focus solely on the functionality and capabilities of Nagios XI.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend Nagios for its scalability and efficiency in monitoring a wide range of infrastructure components, from applications and services to operating systems. The tool’s highly customizable web interface and advanced graphs make it easy for administrators to identify and resolve network incidents quickly.
Who is it recommended for?
Nagios is well-suited for organizations that have mission-critical infrastructure components needing constant monitoring. It is particularly beneficial for administrators and IT departments who want a customizable, multi-user interface for efficient troubleshooting and capacity planning.
Differences between SolarWinds vs Nagios:
Features:
- Automatic Network Scanning and Discovery / Mapping & Topology Diagrams:
SolarWinds is extremely good at Automatic discovery and mapping / topology diagrams. There is easy to find and use discovery features, and the mapping / topology can be auto generated (much easier than most snmp suites, which require you to build your own maps), and also built from scratch if you so desire.Nagios can do IP sweeps, but you will need to manually specify the ranges and subnet masks, and force it to scan. As for topology, Nagios also has an auto-generated diagram option, which is quite nice. You may also do custom mapping with Nagios.
- Monitoring via SNMP, WMI, and ICMP:
Both are pretty comparable in this regard. They support SNMP, WMI, ICMP, and much more.
- DB Monitoring:
SolarWinds is capable of monitoring SQL, MySql, Oracle, and more. Nagios supports Sql, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB.
- QoS / SLA:
SolarWinds does support QoS monitoring, and can go extremely in depth in that respect. I could not find support for QoS with Nagios, however. As for SLA, Nagios does not have a helpdesk ticketing feature, and the SLA capabilities involve measuring node uptime and keeping track of trends, and custom alerts. SolarWinds also uses custom alerts and reports, and the helpdesk ticketing features are only available if you purchase and download the Web Help Desk software that is a separate base program from the Network Performance Monitor.
- Computer / Server Hardware Health:
Nagios does not appear to have any form of temperature or voltage sensors readily available. There is the possibility to add plugins from Nagios or third parties, which could potentially support this. SolarWinds however, can support a wide variety of hardware health metrics, and can generate reports of uptime and availability with ease.
- Monitoring (CPU, Memory, Network Cards):
Nagios is capable of monitoring CPU usage, memory usage, disk usage, and specific services / processes. SolarWinds can measure all of these as well, and this information is easily added to the dashboard with built-in graphs and charts. A key difference to note here is that SolarWinds can measure network card speed, whereas Nagios is limited to only uptime measurements which SolarWinds also provides.
- Web Server Monitoring (IIS, Apache):
Nagios is capable of monitoring a specific web site, but is not natively able to monitor IIS directly. The same goes for Apache, NGINX, or any form of web server. SolarWinds on the other hand, will require the Server and Application Monitor program which is a base program separate from the Network Performance Monitor to accomplish this sort of scanning.
- Active Directory Monitoring:
Nagios does support LDAP monitoring, and you may monitor replication errors using event traces. However, these must be manually set up, and there is not really a quick method of doing this. SolarWinds will require a purchase of the Server and Application Monitor program to perform this type of scan as well.
- Netflow, IPFIX, sFlow, jFlow Monitoring:
Nagios does not support any form of Netflow, IPFIX, sFlow, or jFlow monitoring. Where Nagios is lacking in this area, SolarWinds is not so much. Netflow is huge with SolarWinds , and it is highly encouraged to take advantage of this. If you wish to monitor with the other protocols, however, you will need to purchase and install the Network Traffic Analyzer program that extends the Network Performance Monitor base program.
- VM HyperVisor Monitoring:
SolarWinds requires the Virtualization Manager program to monitor different types of hypervisors. Nagios is natively able to monitor VMWare and VMWare alone.
- Application Monitoring:
SolarWinds supports this right off the bat. Nagios is capable of keeping track of process and service uptime as well.
- Reports and Graphs of Historic Trends:
Nagios has a very nice repertoire of default reports, with customizable graphs and slightly customizable screen layouts. SolarWinds has an even larger selection of graphs and metrics available, and I would say that report generation and creation is much easier with SolarWinds , as well as faster.
- Mobile App Support:
SolarWinds has apps for both Android and IOS, and they received fairly good reviews on both. Nagios however, does not have any available apps.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SolarWinds NPM outperforms Nagios XI. If you are willing to purchase the different modules and addons for SolarWinds , it absolutely knocks Nagios XI out of the park. If you are looking for one single purchase and install, then Nagios XI might be your better bet, however, if you can make use of the breadth of scanning features that it’s single install contains compared to SolarWinds single install of the Network Performance Monitor.
SolarWinds would also be the better option in my opinion due to the fast and easy install, which can be done on a Windows OS and doesn’t require familiarity with Linux or CentOS, and has a nicer UI.
In my opinion, the benefits from SolarWinds are worth the slightly higher overhead in system resources that comes with the program as well, compared to Nagios. Another plus is that while Nagios does pricing by node count, SolarWinds is a one-time flat purchase.
We highly recommend using SolarWinds, since you will save money in the long run, and have a much easier and more efficient use of the program than with Nagios XI.