The complexity of networks is growing by the day, thanks to the emergence of new technologies, changes in workplace policies, and the growth of the organization spanning across different geographical regions.
While this is all good from an organizational standpoint, managing these networks and staying on top of all that is happening on them becomes extremely difficult, if not impossible, for network administrators. It is no longer possible for these administrators to manage the network all by themselves. They need as much help as possible, and much of it can come in the form of network troubleshooting tools.
Best Tools for Network Troubleshooting Tools & Software:
Here are some tools for diagnosing LAN and WAN issues in your network. Make sure to have these tools in your arsenal always, as they can save a ton of time and effort for you.
- Ping
- Traceroute
- Ipconfig
- Nslookup
- Netstat
- PuTTY
- Subnet and IP Calculator
- Speedtest
- Pathping
- Route
Let’s take a detailed look at each of these tools.
1. Ping
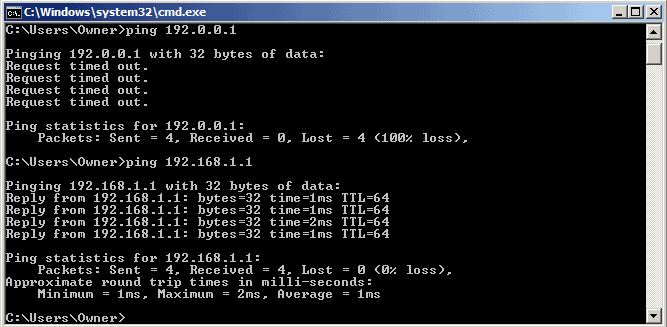
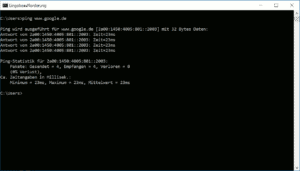
Ping is a utility that tests whether a particular host is available and can accept requests. This is a popular utility often used to check the connection between a source and a destination. It works by sending an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo message to a particular IP address on the network and waits for the reply.
Besides knowing about the state of the destination host, it can also be used to check the response time. If the destination takes too much time to respond, it could mean there is a problem with the host or in the network that is sending the message. It also tells you how many packets were sent, how many were received, and how many were lost during transmission.
With this information, you can identify whether the problem is with the destination host or the network and can take steps to fix the same.
2. Traceroute
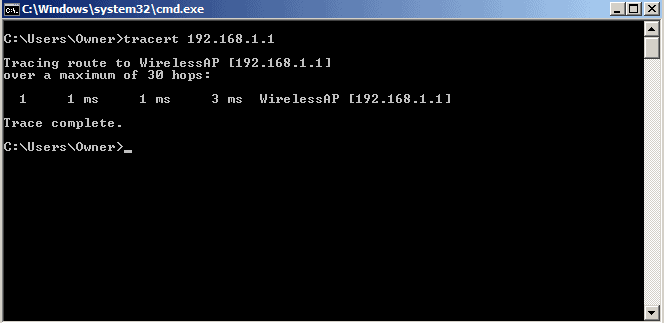
Traceroute or Tracert are diagnostic commands that track the path taken by a packet when it travels from source to destination.
This command is mainly used for displaying the route taken by the package and to measure transit delays in the route. Like ping, traceroute also uses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo packets with time to live (TTL) values. It records the time taken for every hop from source to destination and based on this, network administrators can identify the cause of problems.
It is mostly used to determine response delays and failure points encountered on a network.
3. IPCONFIG
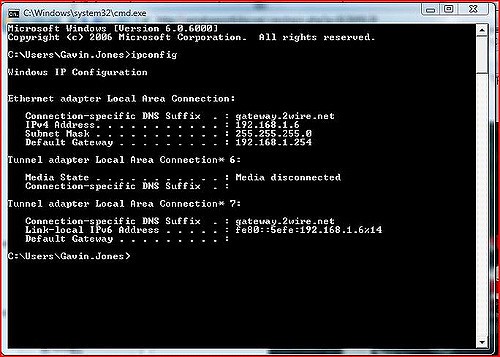
Ipconfig, sometimes spelled as IPCONFIG, is a command-line tool used to display the current configuration settings of your TCP/IP network. It can also be used to modify the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings.
Three parameters can be used with it, and they are “all”, “release” and “renew”. When you use “all” parameter, it displays all the settings. The other two are used when you want to request a new IP address. When you use “/release”, the client immediately gives up the IP address it is using while “/renew” will request a new IP address.
When used without any parameters, it displays IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for all your adapters.
3. Nslookup
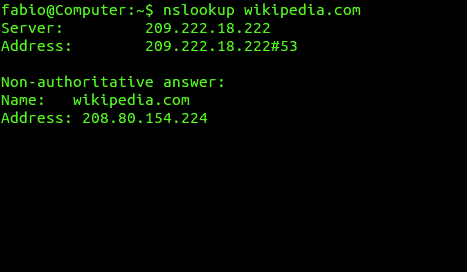
Nslookup stands for Name Server Lookup and is a utility used to query the Domain Name System to get the domain name or any other pertinent record. This tool is mostly used to locate the IP address of a domain by entering its name.
When you enter the name of a domain, this tool will send a query packet to a designated DNS to get the corresponding IP address. You can also enter the IP address and get the domain name. This tool is mainly used for troubleshooting DNS related problems.
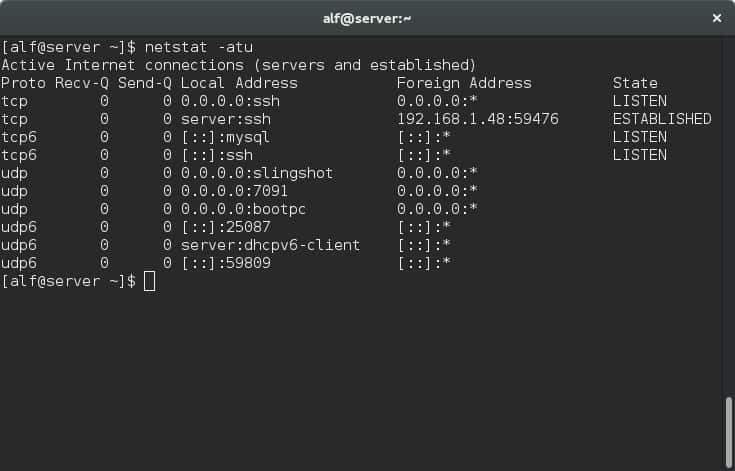
4. Netstat
Netstat is a common utility tool available in all major operating systems such as Windows, Unix, and Linux. As the name suggests, this tool gives information and statistics about the current TCP/IP protocols of your system.
It comes with many parameters, and they are:
- -a: Shows all the connections and listening ports
- -b: Shows the executable involved in creating each connection.
- -e: Shows the Ethernet statistics
- -n: Shows addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
- -o: Shows the owning process ID associated with each connection
- -p value: Shows connections for the specified protocol. Here, the value is the protocol such as UDP, TCP, and so on.
- -r: Shows the routing table
- -s: Shows statistics for every available protocol.
- -v: Should be used with -b option to see the sequence of components involved in creating a connection.
Overall, netstat is a great forensic tool to know more about the programs and processes that are active on a computer.
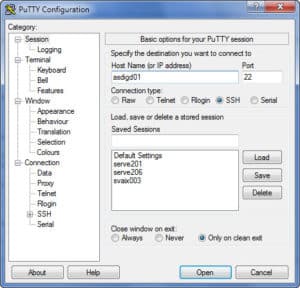
5. PuTTY
PuTTY is an open-source terminal emulator and console. It supports many protocols such as Telnet, rlogin, SSH, and SCP and this makes it ideal to connect with remote connections using your private SSH keys.
The latest version support 64-bit clients and elliptic curve cryptography for additional security.
6. Subnet and IP Calculator
A subnet and IP calculator can make it easy to calculate the IP address at any given time, so you can configure the right one. It even allows you to enter a subnet range and see all the IP addresses within that range. You can choose to type your range directly or use the mask pull-down, just depends on you.
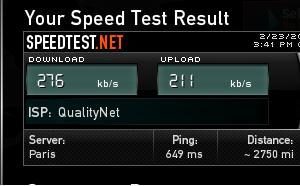
7. Speedtest
Speedtest, as the name suggests, is a tool that helps to calculate the speed of your connection. Using this tool, you can know your Internet speeds and the bandwidth available for a specific host.
This tool is most useful to know how long it will take to upload or download files from a local to a remote host or vice-versa. It also helps you to stay on top of your Internet provider’s offerings and whether it is in tune with the service level agreements.
You can also use the ping test tool to know the quality of your connection as it calculates the response time.
With both these tools, you can calculate the bandwidth and speed during peak traffic and can make the necessary capacity planning as well.
8. Pathping
Pathping is a tool that combines the functionality of a tracert with ping and is mainly used to see the path between two hosts.
It is a versatile tool that gives you control over information such as:
- The maximum number of hops
- Milliseconds wait between pings
- Timeout ranges
- Number of queries per hop
- Connectivity tests
- Use of IPv4 or IPv6 protocols.
9. Route
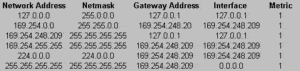
Route is another popular utility tool used to display the status of the routing table. This command can also be used to manually add, edit, or delete entries in the routing table.
A routing table consists of five items – Network address, Netmask, Gateway address, Interface, and Metric. Here is what a routing table looks like.
Conclusion
Thus, these are some of the Basic Networking Troubleshooting Tools and Software that every administrator should have to stay on top of their network and to troubleshoot problems at the earliest.
Many, if not all, these Network Troubleshooting and Diagnostic Tools are Free and may come pre-bundled with your Operating system – You can run them via Command-line or their respective GUI interfaces!