Networks have become ubiquitous in our world today. But do you know that networks can be of different types, mapping, and design to meet the specific needs of an organization or group using it?
Well, in this article, we are going to take a deep dive into network topology and talk extensively on the pros and cons of each, so you can accordingly decide how your network must be designed.
What is Network Topology?
In simple words, the network topology is the arrangement of different devices/elements and how they communicate.
This arrangement is often represented in a diagram called the network topology diagram, where the devices in the network are represented as nodes and their communication channels as links.
The idea of a network topology is to help you visualize how a network is set up, so you can accordingly make business decisions such as its expansion or re-arrangement to meet your business’s budget, scale, and goals.
Types of Network Topology
Network topology can be physical or logical, depending on the placement of different devices. For example, if all devices are in physical proximity and communicate through a transmission medium, it’s called a physical topology.
On the other hand, a logical topology is a way data travels between devices located far away from each other and are not physically connected through a medium.
As a network administrator, you can build a physical or logical network topology as your business requires.
Let’s now look at the different topologies.
Bus Network Topology
This physical topology is also called the backbone topology as it physically connects every device in a network to the main cable. In addition, each device is connected by a drop cable, which is referred to as line topology.
Advantages of Bus Network Topology
The advantages of this type of network topology are:
- The simplest way to connect devices and can come in handy for connecting devices in a linear fashion.
- Highly efficient and fast
- Requires much less cable than other types, thereby making it cost-effective and easy to set up.
- Easy to connect or remove a device at any time without impacting other devices
- Easily expandable
- Works best for small networks.
Disadvantages of Bus Network Topology
The disadvantages of bus network topology are:
- It doesn’t scale well for the extensive network
- Troubleshooting is hard
- Packet loss rates are high
- Slow when compared to other topologies
- Too much reliance on the main cable
- Terminators are required at both ends of the main cable.
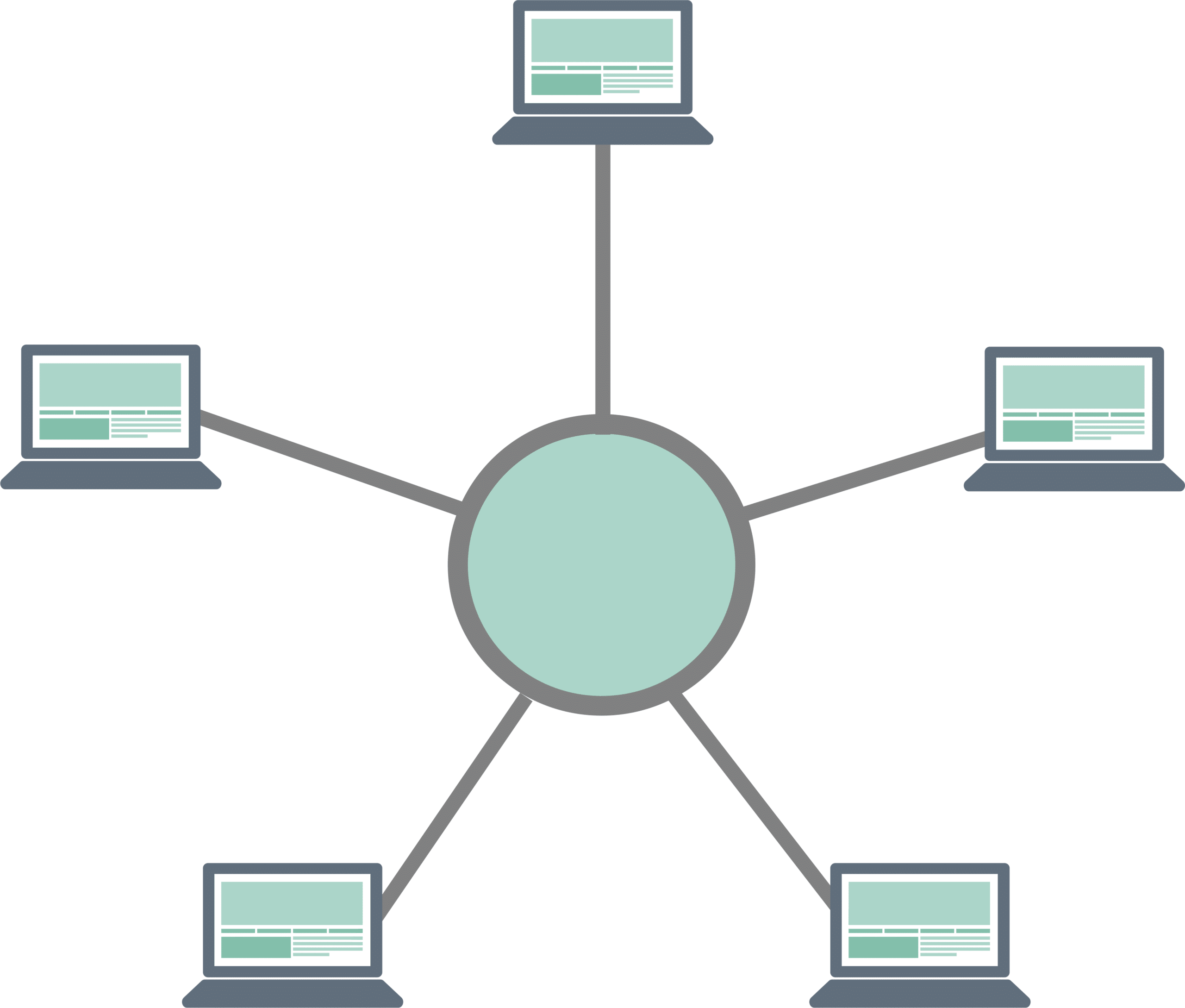
Star Topology
As the name suggests, this topology is shaped like a star where each device connects to a hub, and in turn, the hub connects to the main cable.
Advantages of Star Network Topology
The advantages of star network topology are:
- Highly reliable, as the network will work even if one cable fails
- No data collisions
- Robust and easy to set up
- Easy to detect faults
- No disruptions to the network while adding or removing new devices
- Only one I/O port is required, so it is less expensive than many other topologies.
Disadvantages of Star Network Topology
The disadvantages of star network topology are:
- Requires more cable than the bus topology
- The hub is a single point of failure that can impact the communication of other devices
- The hub requires more resources and regular maintenance
- Extra switches are required
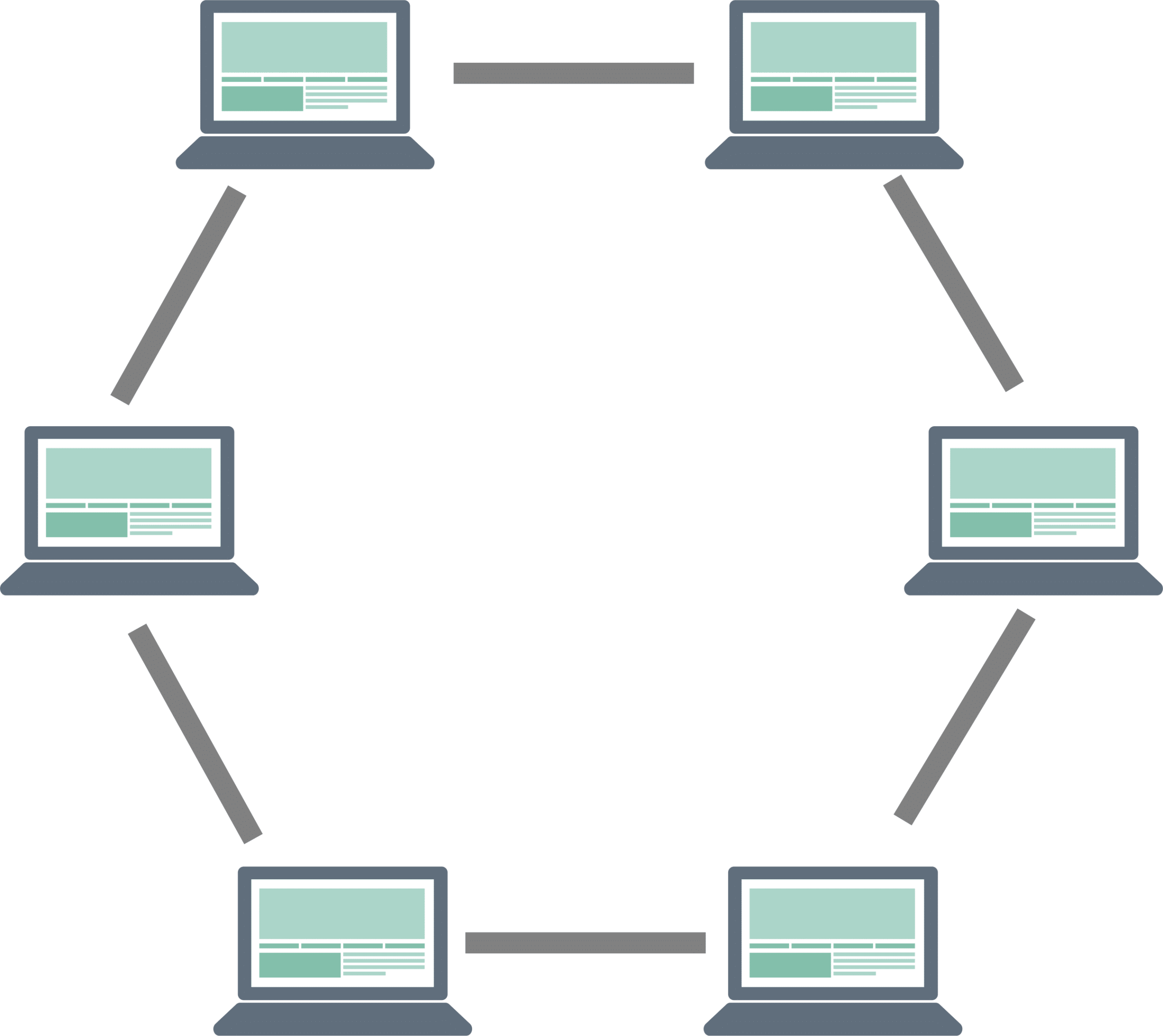
Ring Network Topology
All the devices are connected to form a circular or ring path for data transmission in this topology. In addition, every device in this topology is connected to its two immediate neighbors on the left and right.
Advantages of Ring Network Topology
The advantages of ring network topology are:
- First, there are no packet collisions as data can flow in one direction only.
- Every device gets equal access to resources
- There is no central hub involved
- These are orderly and well-organized
Disadvantages of Ring Network Topology
The disadvantages of ring network topology are:
- Every packet has to pass through the entire ring, and this can take additional time
- Failure of one workstation can impact the whole network
- Expensive, as all the devices have to be connected
- Adding or removing networks would require considerable time and effort
- Extremely difficult to troubleshoot
- High dependence on a single cable
- Not scalable
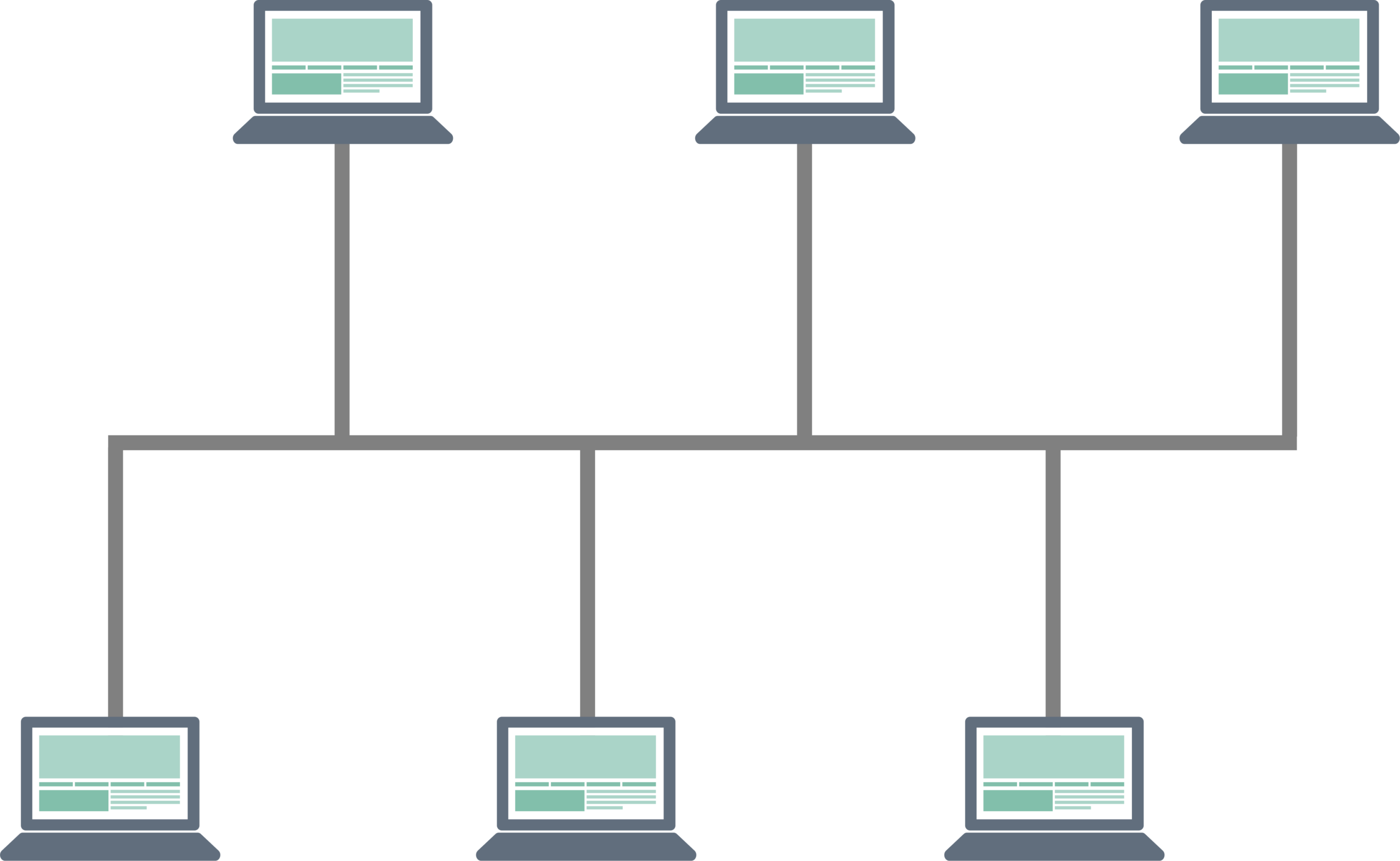
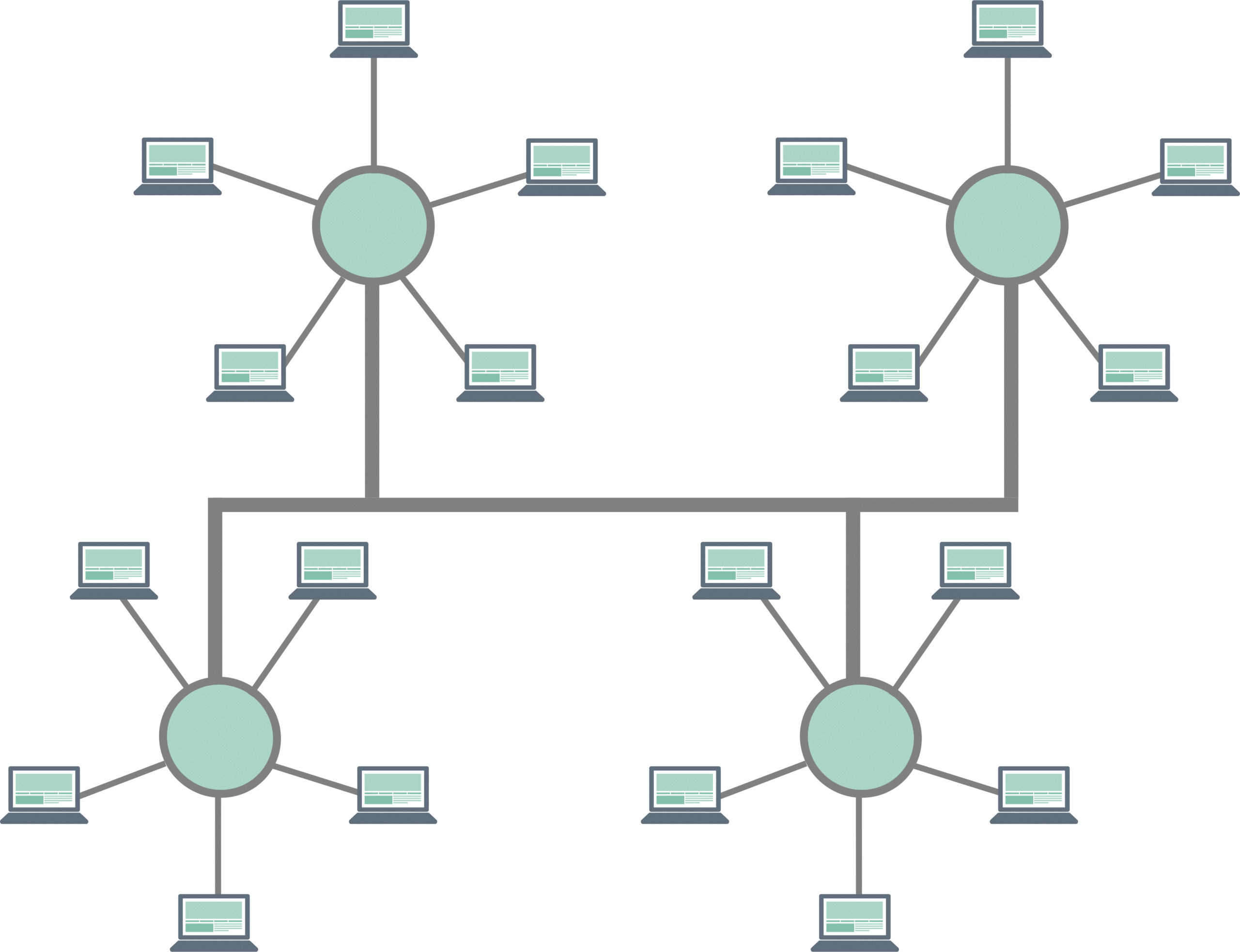
Tree Network Topology
As the name suggests, tree topology is one where the devices are connected in the form of a tree. It is a combination of a bus and a star network topology, and all the devices are connected as branches to the main tree and connect with other devices as smaller branches. It is also one of the most popular types of network topologies.
Advantages of Tree Network Topology
Some of the advantages of tree network topology are:
- Provides a hierarchical structure as well as a central arrangement to leverage the benefits of both.
- Highly scalable
- Leaf nodes can be added at any time to the branches
- Failure of one node doesn’t affect the others
- Easy to maintain
- Fault identification is quick and easy
- Supported by most hardware and software
- Offers flexibility in wiring
Disadvantages of Tree Network Topology
The disadvantages of the tree network topology are:
- Hard to configure
- The scalability depends on the length of the cable
- Failure of the leading line or tree trunk can affect the entire network.
- Network performance is impacted when more devices are added
- Requires more cabling, and hence can be expensive
Hybrid Network Topology
A hybrid network topology combines two or more topologies to leverage the benefits of different structures and create a topology conducive to your organization.
While the exact advantages and disadvantages would vary from one hybrid topology to another, the broad benefits and drawbacks are here.
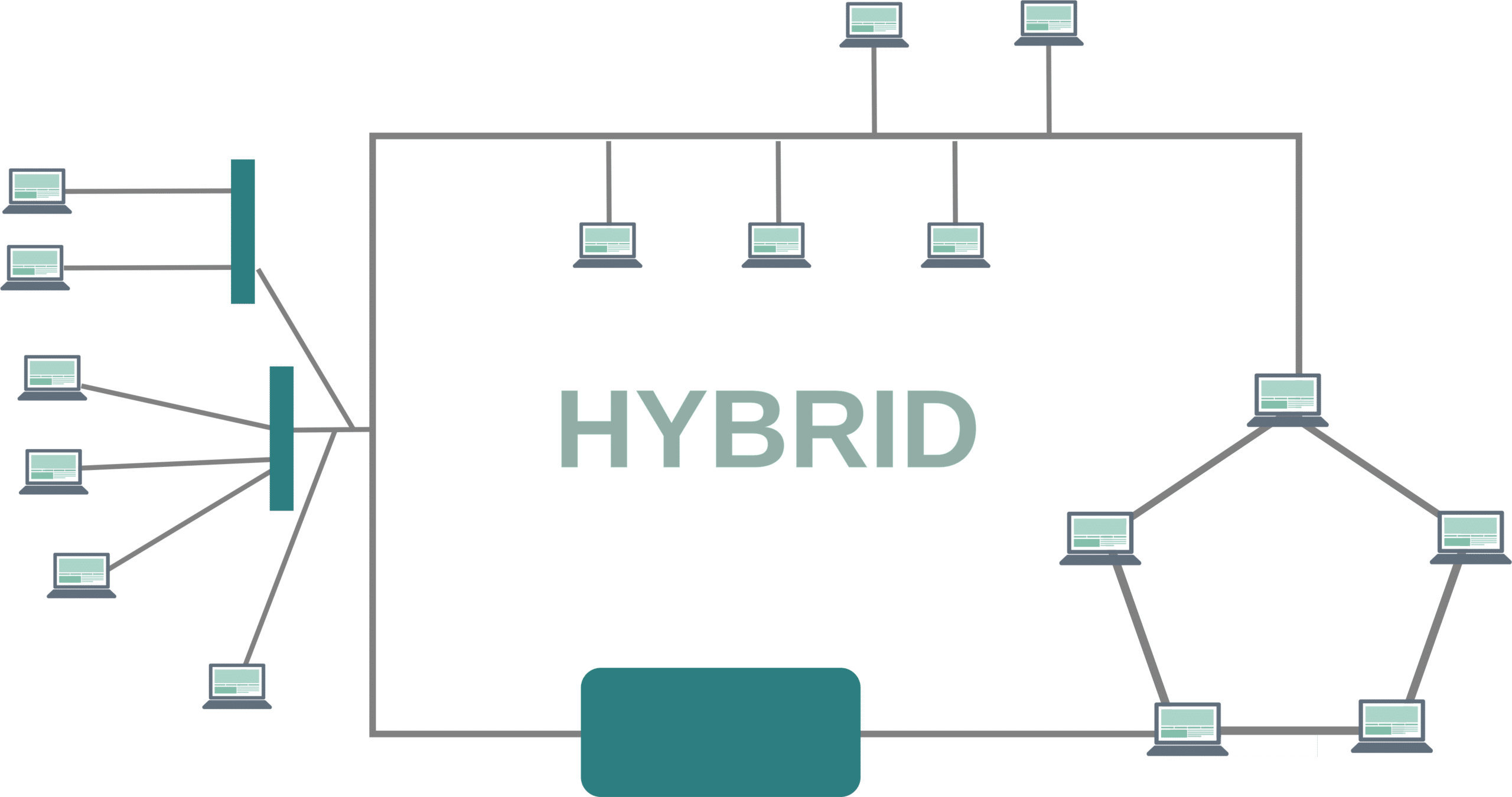
The advantages of hybrid network topology are:
- Leverages the benefits of two or more networks
- Highly flexible to suit an organization’s needs
- Scalable and can be extended quickly
- Ideal for creating large networks
- Troubleshooting is easy
- Reliable and capable of handling large volumes of traffic
Disadvantages of Hybrid Network Topology
The disadvantages of the hybrid network topology are:
- It can get unwieldy without proper planning
- Design is complex and entails skilled resources
- Some configurations can also require hardware changes, thereby adding to their costs
- It may require more cables, depending on the configuration.
- Installation and maintenance are difficult
Mesh Network Topology
In a mesh network topology, all devices are connected, thereby forming a mesh-like pattern. In general, when there are N nodes in a network, there are N * (N-1)/2 links. So, for example, if a network has ten nodes, it would require 45 links.
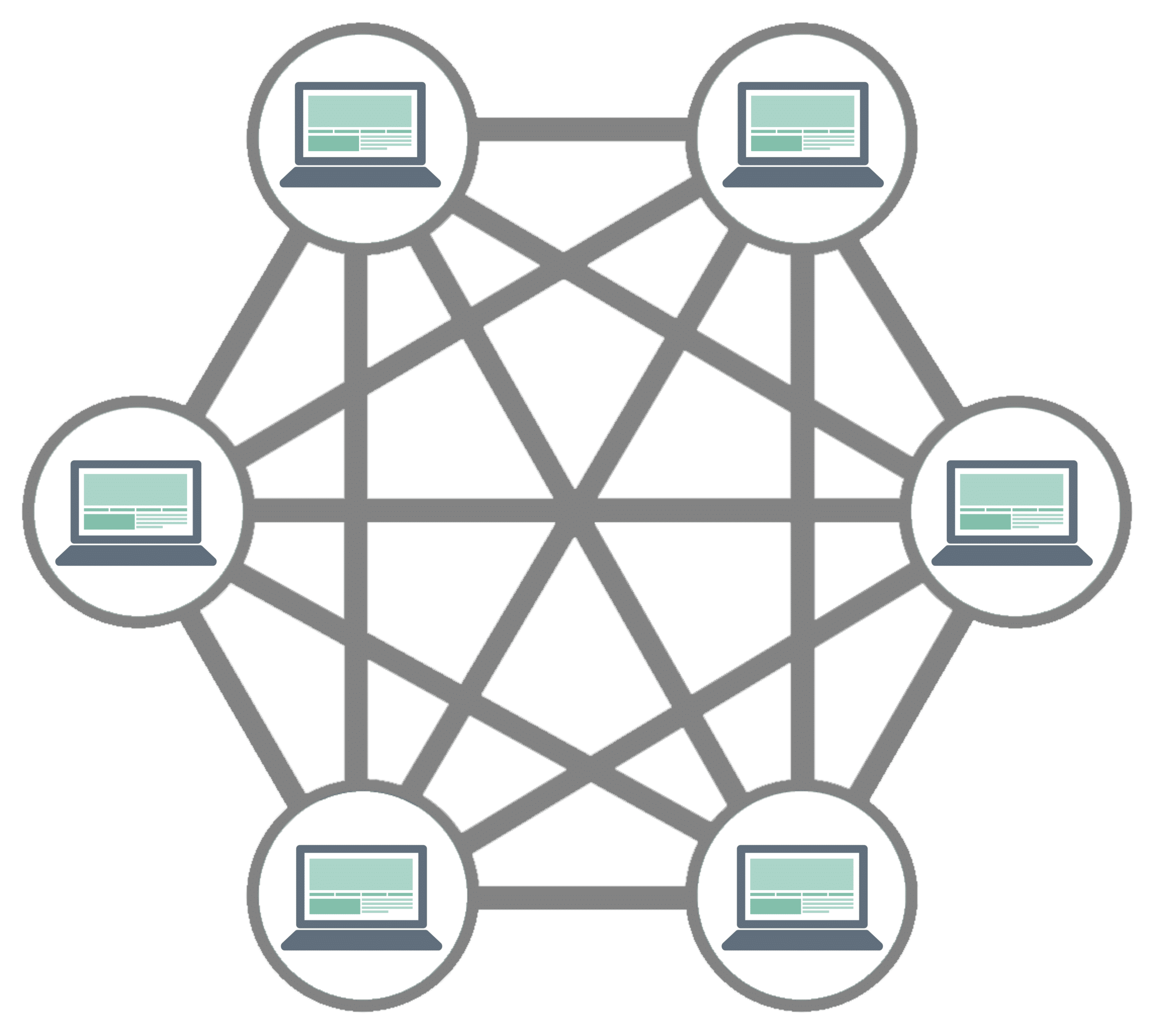
A fully connected network is one where every device is connected to every other device in the network. A partially connected one is where some nodes are connected with others. The advantage of a fully connected network is redundancy and resiliency, while a partial mesh network can be a cost-effective solution.
Advantages of Mesh Network Topology
The advantages of mesh network topology are:
- The failure of a single device will not impact the entire network
- The flow of traffic is quick and straightforward
- Easy to troubleshoot
- Provides redundancy, resilience, reliability, privacy, and security
- Easy to add new devices
- No centralized authority
Disadvantages of Mesh Network Topology
The disadvantages of mesh network topology are:
- Requires more cabling and hence, can be expensive
- Installation can take time
- High power requirements
- Maintenance is challenging as well.
Thus, these are the different network topologies and their advantages and disadvantages.
Moving on, let’s see how you can choose the correct topology for your network.
Choosing the Right Network Topology for Your Organization
Earlier, we saw the different network topologies, and now comes the big question – how to choose the one that best fits your organization’s needs?
Here are some aspects to consider while making this decision.
Cost
One of the most important considerations is cost. If you’re a startup or working with a limited budget, you might want to use a cost-effective topology. But, at the same time, ensure that it doesn’t impact your organization’s requirements for speed and reliability.
To give you an example, when you’re on a shoestring budget, using fiber-optic cables for a mesh network will be unnecessary. Instead, you can choose to use coaxial cables that cost cheaper or choose a star network for cable efficiency.
Cables
Cables are an essential part of the topology. But you can choose from the cable type and length, and accordingly, the cost and performance will vary. For example, coaxial or twisted cables are far cheaper than fiber optic cables and can be a cost-effective solution. However, fiber optic cables offer the highest rates of data transmission and provide more bandwidth. So, depending on the needs of your organization, decide on the cable type.
The same applies to cable length too. Longer cables take a longer time to set up like your mesh network. From this perspective, a bus or star topology might be the easiest.
Hardware Resources
Besides cables, there are other hardware resources that you may need, such as switches and hubs. But, again, you can choose a topology depending on what’s already available, compatibility aspects with your existing infrastructure, and your budgets.
For example, the star topology would require investing in a hub while no such investment is needed in a ring topology.
Scalable
Scalability is another crucial aspect to consider. For example, if you’re growing or anticipate rapid growth shortly, investing in a scalable network topology such as a tree or hybrid topology makes sense. On the other hand, if you’re an established company with a steady growth rate, any of the different topologies can be chosen after considering other aspects.
Time and Effort Considerations
Some topologies entail more time and effort, especially in terms of setup and maintenance. A case in point is the hybrid topology. If you have the resources with the required skills and believe that this topology is the most suited to your organization, go ahead. Otherwise, you may have to balance it out with other aspects.
Thus, these are some aspects to consider while deciding on the correct network topology for your organization.
Mapping the Network Topology
The first step to setting up a network topology is to map it.
Mapping the network topology is the practice of representing the network topology with all its nodes and links. This map is reviewed, and any potential downsides are identified and accounted for.
Here are the broad steps for creating and mapping a network topology.
- Do extensive research to identify the correct network topology for your organization.
- Select a network diagram template and give a name to it.
- Assess the template and remove the unwanted nodes and links.
- Add the extra nodes and links you may need
- Give a name to the items on your network
- Draw the connections or links between the nodes
- Share your network diagram for review.
Once the map is reviewed and approved, it’s time to translate it to a network.
Third-party Tools
While the above mapping process may seem easy, in reality, it is anything but that, given that the requirements tend to be complex. This is where third-party tools can come in handy.
ManageEngine OpManager – FREE TRIAL
ManageEngine OpManager is an automated network topology mapper that discovers devices and creates a map depicting their organization and dependencies – all with minimal effort. A highlight of OpManager is that it modifies these views to meet different audiences. For example, the Business View helps CXOs make informed decisions while the Layer 2 maps enable IT technicians to troubleshoot more efficiently. This ability to tailor content for different audiences is what makes OpManager a popular choice today.
ManageEngine OpManager’s Key Features:
- Layer 2 Devices: Identifies the layer 2 devices and creates a visual representation, along with their nodes, interconnected layers, port-to-port connectivity, and more.
- Automated Mapping: Automatically discovers devices and creates a map to depict their organization and structure.
- Varying Views: Adapts the data to different views for different audiences.
- Multiple Protocols: Supports a wide range of protocols, like CDP, LLDP, IPROUTE, FDB, ARP, and more.
- Performance Evaluation: With a detailed topology map, your IT administrators can quickly identify the root cause of a problem.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend ManageEngine OpManager for its extensive capabilities to discover and map devices accurately with little human intervention. In particular, we love its adaptive views as they make the data far more relevant to different audiences. When this data is combined with the monitoring capabilities of OpManager, it can provide detailed insights for performance improvement and efficient troubleshooting.
Who is it recommended for?
It is a good choice for organizations with extensive networks. It can be helpful for large organizations with multi-site deployments and diverse environments that span across different regions.
OpManager is also affordable. Its Standard edition starts at $95, while the Professional edition starts at $145. Download a 30-day free trial to get started.
SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper
While the above mapping process may seem easy, in reality, it is anything but that, given that the requirements tend to be complex.
The good news is that many third-party tools like the SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper can handle this network mapping process for you. First, you would have to specify the type of network topology, the number of nodes, the length of the cables, and other pertinent information. Then, the tool will draw an efficient network map for you to set up your organization’s network.
Let’s look at the features of this tool.
SolarWinds Network Topology Manager’s Key Features:
The salient features of SolarWinds Network Topology Manager are:
- Automatically discovers the existing network topology, so you can quickly add or remove nodes and connections
- Creates comprehensive and detailed network topology maps
- Allows you to edit the details of objects on the map
- Makes it easy to connect network devices manually
- Builds multiple network maps with a single scan
- Comes with the capability to perform multi-level network discovery
- Auto-detects changes to the network topology
- Provides the option to export the network map to Visio
- Addresses your regulatory compliance
- Optimizes and simplifies the network mapping process
- Enables you to visualize your network with the map
- Automates inventory management
- Improves the overall performance of your network
- Helps with troubleshooting as well
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper offers a robust suite of features designed to simplify and optimize the network mapping process. With capabilities like automated discovery, multi-level network discovery, and export options to Visio, it is a comprehensive tool for anyone managing a network.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for network administrators, IT managers, and compliance officers who need a detailed, up-to-date view of their network topology. Its feature set also makes it suitable for organizations that require automated inventory management and those with complex compliance requirements.
The SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper is priced at $1,570. You can download a 14-day free trial.
Conclusion
To conclude, creating a network topology map is the first step towards building a robust network for any organization.
But this is not easy as you have to figure out the correct topology for your organization, create a map depicting the nodes and connections, and get it approved by the concerned people. This has to be done after evaluating many aspects like cost, your organization’s requirements, the available resources and the ones needed for this setup, and more.
The good news is this doesn’t have to be a complex process, thanks to the availability of tools such as the ManageEngine OpManager.
This tool automatically discovers your organization’s existing topology, making it easy to add or remove nodes and connections, find new devices, and generate maps based on your inputs. Its intuitive user interface masks the complexity behind developing a network map, which is why it is a valuable tool for every organization.